news
Amazon Web Services - thwarting spam with a decade-old best practice
In this News Article
Jump to
Introduction
When things move to the "cloud", sadly, good things don’t always follow. Miscreants of various sorts have long recognized that they too can benefit from the same advantages as regular users: scalability, abstraction and pay-per-use. It was thus no surprise that spamming operations set-up shop on the biggest of all clouds: Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Difficulties in detection
This is not news per se, but these malicious operators quickly found their way into the extensive array of APIs offered by AWS. By building their set-up specifically around the AWS ecosystem, cybercriminals rapidly maneuvered within it. As a result, mitigation was difficult not only for those receiving their spam but also for the AWS abuse team, which, on occasion, had difficulty pinpointing the offending accounts.
History repeating itself
What’s interesting is that this isn’t the first time we’ve observed this kind of situation; it isn’t a million miles away from the "spambots in end-user systems" which have been around for over 10 years. Spambots have infected end-users' systems for years, taking advantage of network and IP address diversity to get the spam out. Similarly to there being no necessity for the majority of end-user systems to send mail directly, neither does the majority of cloud infrastructure.
Tipping point at AWS
Top ASNs appearing in Spamhaus CSS Listings
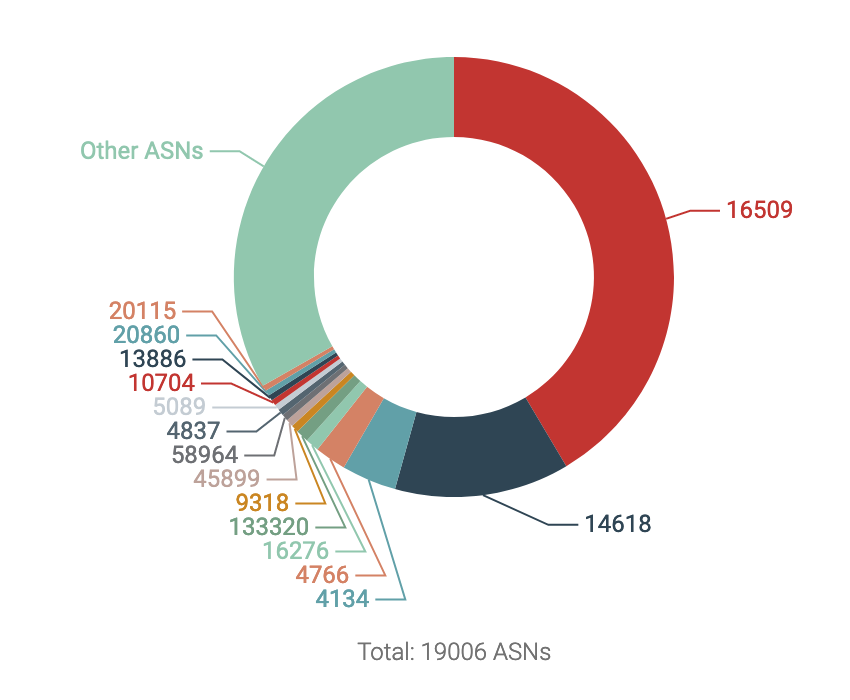
Spamhaus has an automated listing of IP addresses that are involved in sending low-reputation email; this data set is called CSS. In early 2020, a critical tipping point was reached; over 50% of Spamhaus’ CSS listings were made up of IPs that existed on two autonomous system (AS) numbers; AS16509 and AS14618. Both of these AS numbers are used by AWS. But, Spamhaus wasn’t the only organization to notice!
Restricting Port 25
At the end of January 2020, AWS announced that they would start restricting port 25 access, by default. Why restrict port 25? Well, port 25 is the channel designated for sending email. By restricting this port, operators force email to go through dedicated outbound mail-servers instead of direct-to-mx, thereby greatly limiting the damage that can be done.
In AWS's FAQ regarding this change, it explains that it is taking this action "to protect customers and other recipients from spam and email abuse." Does this sound familiar? It should; this is what the majority of internet service providers (ISPs) have done for years to their end-user networks. By deploying this relatively simple countermeasure, massive amounts of abuse are not only mitigated but will simply never occur in the first place.
A nod to AWS
AS16509 & AS14618 CSS Listings decrease
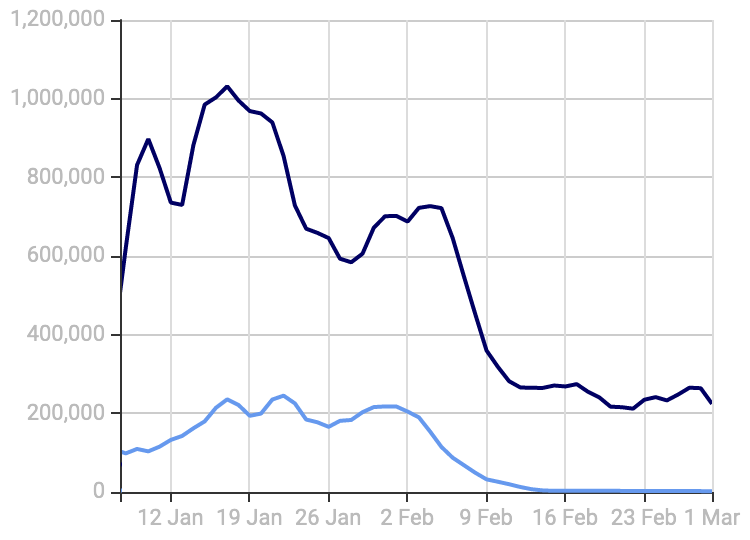 Spamhaus applauds the efforts of the various AWS teams involved in this endeavor. As the graph to the right illustrates, blocking port 25 outbound has had a significant effect on the malicious traffic we have been observing across AS16509 and AS14618 - and the numbers are still reducing. This will save the world from a lot of spam while making the AWS cloud space significantly cleaner.
Spamhaus applauds the efforts of the various AWS teams involved in this endeavor. As the graph to the right illustrates, blocking port 25 outbound has had a significant effect on the malicious traffic we have been observing across AS16509 and AS14618 - and the numbers are still reducing. This will save the world from a lot of spam while making the AWS cloud space significantly cleaner.
Don’t make resources available to miscreants
There are valuable lessons to be learned here for the wider internet community; abusers will go wherever they can get the resources. With this in mind, products and architecture should always be designed factoring in abuse i.e., how cybercriminals could work the product/architecture to their advantage. Customers should always be vetted and infrastructure constantly monitored for abuse, and where abuse is reported, speedy remediation should take place.
Finally, a thought for us all: the best spam is the spam that is never sent in the first place.